前言
记录时间:2023.3.1
已坚持的第三天
java从入门到精通
学习java时间历程记录打卡
早上6:00到 12:00
下午1:00到6:00
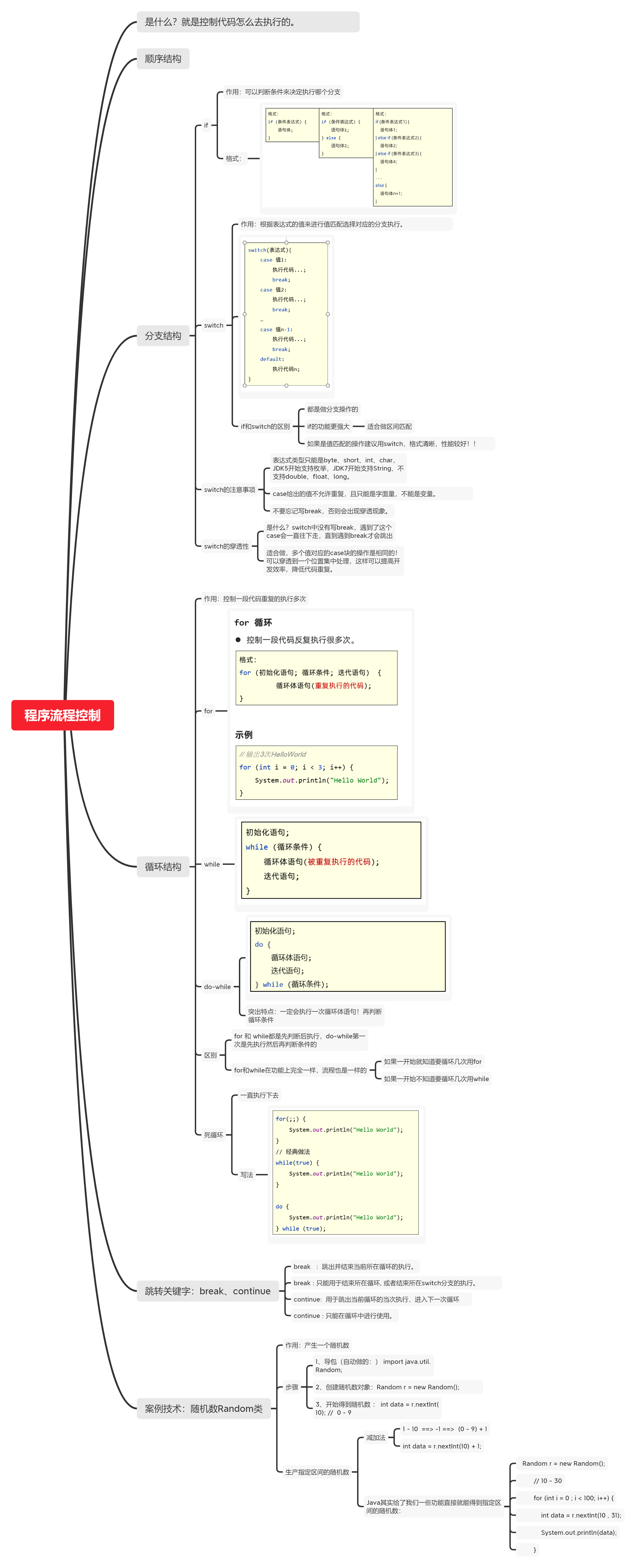
java程序流程控制总结
完成代码练习
1.分支结构
1.if条件语句
package com.vqqc.branch;
public class ifDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:心跳(60-100)之间正常的。否则系统进一步检查
//格式1:if(条件表达式){代码...}
int heartBeat = 90;
if(heartBeat <60 || heartBeat > 100){
System.out.println("您的心跳数据是:" + heartBeat +"您可能需要进一步检查!");
}
System.out.println("检查结束");
//格式2:if(条件表达式){ 代码... } else { 代码... }
//需求:发红包
double money = 1;
//发一个1314
if(money >=1314){
System.out.println("您当前发送红包成功~~~");
}else {
System.out.println("您的余额不足!");
}
//格式3:if(条件表达式){ 代码... } else if { 条件表达式 }{ 代码.... } else { 代码... }
//绩效系统: 0-60 C 60-80 B 80-90 A 90-10 A+
int score = 99;
if(score >=0 && score < 60){
System.out.println("您的本月绩效是:C");
}else if(score >= 60 && score <=80) {
System.out.println("您的本月绩效是:B");
}else if(score >= 80 && score <=90) {
System.out.println("您的本月绩效是:A");
}else if(score >= 90 && score <=100) {
System.out.println("您的本月绩效是:A+");
}else {
System.out.println("您录入的分数有问题!");
}
}
}2.switch分支结构
package com.vqqc.branch;
public class SwitchDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//学会使用switch分支结构 ,理解流程
// 周一:埋头苦干,解决bug 周五:今晚吃鸡
// 周二: 请求大牛程序员帮忙 周六:与王婆介绍的小芳相亲
// 周三:今晚啤酒、龙虾、小烧烤 周日:郁郁寡欢、准备上班。
// 周四: 主动帮助新来的女程序解决bug
String weekday = "周三";
switch (weekday){
case "周一":
System.out.println("埋头苦干,解决bug");
break;
case "周二":
System.out.println("请求大牛程序员帮忙");
break;
case "周三":
System.out.println("今晚啤酒、龙虾、小烧烤");
break;
case "周四":
System.out.println("主动帮助新来的女程序解决bug");
break;
case "周五":
System.out.println("今晚吃鸡");
break;
case "周六":
System.out.println("与王婆介绍的小芳相亲");
break;
case "周日":
System.out.println("郁郁寡欢、准备上班。");
break;
default:
System.out.println("数据有误!");
}
}
}3.清楚switch的注意要点
package com.vqqc.branch;
public class SwitchDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//清楚switch的注意点,并在开发的时候注意
//表达式类型只能是byte、short、int、char,JDK5开始支持枚举,JDK7开始支持String、不支持double、float、long。
//long lg = 20;
//switch (lg) {
//}
//case给出的值不允许重复,且只能是字面量,不能是变量。//int a1 = 3;
switch (3){
case 31:
break;
case 3:
break;
}
//不要忘记写break,否则会出现穿透现象
String weekday = "周三";
switch (weekday) {
case "周一":
System.out.println("埋头苦干,解决bug");
break;
case "周二":
System.out.println("请求大牛程序员帮忙");
//break;
case "周三":
System.out.println("今晚啤酒、龙虾、小烧烤");
//break;
case "周四":
System.out.println("主动帮助新来的女程序解决bug");
break;
case "周五":
System.out.println("今晚吃鸡");
break;
case "周六":
System.out.println("与王婆介绍的小芳相亲");
break;
case "周日":
System.out.println("郁郁寡欢、准备上班。");
break;
default:
System.out.println("数据有误!");
}
}
}4.switch的案例
package com.vqqc.branch;
public class SwitchDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:用户输入月份可以展示该月份的天数。
// 1、3 、5、 7 、 8、 10、 12月份是 31天
// 2月份是闰年为29天、非闰年为28天。
// 4 、6 、9、 11月份 是30天
int month = 7;
switch (month) {
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
System.out.println(month + "是31天!");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(month + "月份是闰年为29天、非闰年为28天");
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
System.out.println(month + "是30天!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("数据有误!");
}
}
}2.循环结构
1.学会使用for循环
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class ForDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//学会使用for循环,并理解它的执行流程
//需求:输出三次Hello,World
for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++ ){
System.out.println("Hello,world"); //3次循环
}
System.out.println("------------------------------");
for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ ){
System.out.println("Hello,world"); //5次循环
}
System.out.println("------------------------------");
for (int i = 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++ ){
System.out.println("Hello,world");//5次循环
}
System.out.println("------------------------------");
for (int i = 1 ; i <= 5 ; i+=2 ){
System.out.println("Hello,world");//5次循环
}
}
}2.用for循环的案例1
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class ForTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:计算1-5的和
//2.定义一个整数变量用于增加数据变量的求和
int sum = 0;
//1.定义一个for循环找到1 2 3 4 5
for (int i = 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++ ){
// i = 1 2 3 4 5
//3.把循环的数据累加给sun变量
/*
等价于:sum = sum + i
i == 1 sum = 0 + 1
i == 2 sum = 1 + 2
i == 3 sum = 3 + 3
i == 4 sum = 6 + 4
i == 5 sum = 10 + 5
*/
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1-5的和是" + sum);
}
}3.用for循环的案例2
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class ForTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:求 1-0的奇数和
//3.定义一个求和的变量累加奇数的和
int sum = 0;
//1.定义一个循环找到 1 2 3...10
for (int i = 1 ; i < 10 ; i++){
//i 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
//筛选出奇数
if(i % 2 == 1){
//i = 1 3 5 7 9
sum += i;
}
}
//4.输出求和变量即可
System.out.println("1-10的奇数和是:" + sum);
System.out.println("---------------------");
//1.定义循环找到 1 3 5 7 9
int sum1 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10 ; i+=2) {
sum1 += i;
}
System.out.println("1-10的奇数的和是:" + sum1);
}
}4.用for循环的案例3
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class ForTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求找出水仙花数并输出
//循环外的定义一个变量用于记录水仙花的个数
int count = 0;
//1.定义一个for的循环找出全部三位数
for (int i = 100; i <= 999 ; i++) {
//2.判断三位数是否满足要求
//个位
int ge = i % 10;
//十位
int shi = i / 10 % 10;
//百位
int bai = i / 100;
if((ge*ge*ge + shi*shi*shi + bai*bai*bai) == i){
System.out.print(i + "\t");
count++;
}
}
System.out.println();//换行
System.out.println("水仙花个数是:" + count); //153 370 371 407 水仙花个数是:4
}
}5.学会使用while循环
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class WhileDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:学会使用while循环,并理解使用
int i = 0;
while (i < 3){
System.out.println("Hello World!");//循环三次
i++;
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
int j = 0;
while (j < 3 ){
System.out.println("Hello World!");//无限循环
}
}
}6.用while循环案例
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class WhileTest6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需要:珠穆朗玛峰高度8848860 纸张厚度为0.1 折叠纸张直到不低于珠穆朗玛峰的高度,求折叠几次
//1.定义变量记录山峰的高度 纸张的厚度
double peakHeight = 8848860;
double paperThickmess = 0.1;
//3.定义一个变量用于折叠纸张的次数
int count = 0;
//2.定义一个while循环控制纸张进行折叠
while (paperThickmess < peakHeight){
//让纸张厚度多一倍
paperThickmess *= 2;
count++;
}
System.out.println("折叠的次数:" + count);
System.out.println("纸张的最终的厚度:" + paperThickmess);
}
}7.学会使用do-while循环
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class DoWhileDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:学会使用dowhile循环,并理解使用
int i = 0;
do {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
i++;
}while (i < 3);
System.out.println("------------------------");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
System.out.println("---------------------");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
int n = 0;
while (n < 3 ){
System.out.println("Hello Wrold!");
n++;
}
System.out.println(n);
}
}8.学会定义死循环
package com.vqqc.loop;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DeadForDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标: 学会定义死循环
// for ( ; ; ) {
// System.out.println("Hello World!");
// }
//经典死循环写法
// while (true){
// System.out.println("这是一个死循环!");
// }
// do {
// System.out.println("这是一个死循环!");
// }while (true);
System.out.println("---------------------");
//1.定义正确的密码
int okPassword = 520;
//2.定义一个死循环让用户不断的输入密码认证
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.println("请您输入正确的密码:");
int password = sc.nextInt();
//3.使用if判断密码是否正确
if (okPassword == password){
System.out.println("登录成功!");
break; //可以理解结束当前在循环的执行的
}else {
System.out.println("密码错误!");
}
}
}
}9.理解嵌套循环的执行流程
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class ForForDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标:理解嵌套循环的执行流程
//场景:假如你有老婆,然后你犯错了,你老婆罚你5天,每天说3句我爱你
for (int i = 0; i < 5 ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.println("我爱你!");
}
System.out.println("----------------------");
}
/*
*****
*****
*****
*****
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println(); //换行
}
}
}10.break continue 的作用
package com.vqqc.loop;
public class BreakAndContinueDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标: break continue 的作用
// 场景:假如你又有老婆了,然后你犯错了,你老婆罚你做5天家务,每天洗碗,但是洗碗到第三天后心软了原谅你了不用洗了
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("快乐的洗碗~~~~~");
if (i == 2){
break; //跳出并结束当前的执行
}
}
//continue 跳出当前循环的当次执行,进入循环的下一次
//场景:假如你又有老婆了,然后你犯错了,你老婆罚你做5天家务,
// 每天洗碗,但是洗碗到第三天后心软了原谅你了不用洗了, 但是我依然要继续洗第4天 第5天
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3){
continue; //立即跳出单次执行,进入循环的下一次!
}
System.out.println("洗碗" + i);
}
}
}3.生成随机数的案例
1.学会使用java提供的随机数类Random
package com.vqqc.random;
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标: 学会使用java提供的随机数类Random
//1.导包
//2.创建随机数对象
Random r = new Random();
//3.调用nextInt功能(方法)可以得到一个整型的随机数
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int data = r.nextInt(10); // 0- 9 不包含 10 的(包前不包后)
System.out.println(data);
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
//1 - 10 ==> -1 ==> (0 -9 ) + 1
int data = r.nextInt(10) + 1;
System.out.println(data);
// 3 - 17 ==> (0 - 14) + 3
int data1 = r.nextInt(15) + 3;
System.out.println(data1);
}
}2.随机数Random类的案例
package com.vqqc.random;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RandomDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.随机一个幸运号码 1- 100 之间 ( 0- 99 )+ 1
Random r = new Random();
int luckNumber = r.nextInt(100) + 1;
//2.使用一个死循环让用户不断去猜测,并给出提示
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
//让用户输入数据猜测
System.out.println("请您输入猜测的数据(0-100):");
int guessNumber = sc.nextInt();
//3.判断这个猜测号码与幸运号码的大小情况
if(guessNumber > luckNumber) {
System.out.println("您猜测的数据过大!");
} else if(guessNumber < luckNumber) {
System.out.println("你的猜测的数据过小!");
}else {
System.out.println("恭喜你猜中了!");
break; //直接跳出并结束当前死循环!!
}
}
}
}3.Random指定区间的随机数案例
package com.vqqc.random;
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//指定区间的随机随机 10 - 30
Random r = new Random();
//10 - 30
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++ ) {
int data = r.nextInt(10 ,31);
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}视频总结
1.程序流程控制课程介绍
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=39
2.分支结构:if、switch、switch穿透性
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=40
3.循环结构:for循环、求和、水仙花数
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=41
4.循环结构:while循环、珠穆朗玛峰案例
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=42
5.循环结构:do-while循环,三种循环的总结
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=43
6.死循环、循环嵌套、break、continue
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=44
7.案例技术:Random类,猜数字游戏
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=45
8.总结:程序流程控制
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Cv411372m?p=46
视频来源:黑马程序员
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![光遇自动更新每日任务接口[接口分享]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/1670250329-apijktppt.png)
![简单用html写了一个光遇蜡烛查询的网页工具[实用工具]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/1676084107-微信图片_20230211105428.png)
![php基础教程-数组冒泡排序算法[技术分享]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/1670257414-slt..png)
![JS基础教程:2023.4.2坚持第35天-JavaScript web APIs BOM操作[js教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/1680450097-Web-APIs.png)
![JS基础教程:2023.2.27第一天-JavaScript从入门到精通[js教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/1677510437-JS基础.png)
![java入门基础教程:2023.2.27第一天,Java快速入门、IDEA开发工具的使用[java教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/1677498626-画布-1.png)
![JS基础教程:2023.3.5第七天-JavaScript数组和循环使用[js教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/1678026321-JS基础.png)
![JavaWeb开发教程:2023.3.25第二十七天,JavaWeb-vue开发[java教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/1679754603-sheet.png)
![java入门基础教程:2023.2.28第二天,java的基础语法使用[java教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/1677579604-画布-1.png)
![JavaWeb开发教程:2023.3.24第二十六天,JavaWeb-JavaScript[java教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/1679669358-sheet.png)
![Java教程-SSM框架-Spring-相关知识配置使用(二)[java教程]-try栈](https://www.vqqc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/1691808246-1629720945720.png)




暂无评论内容